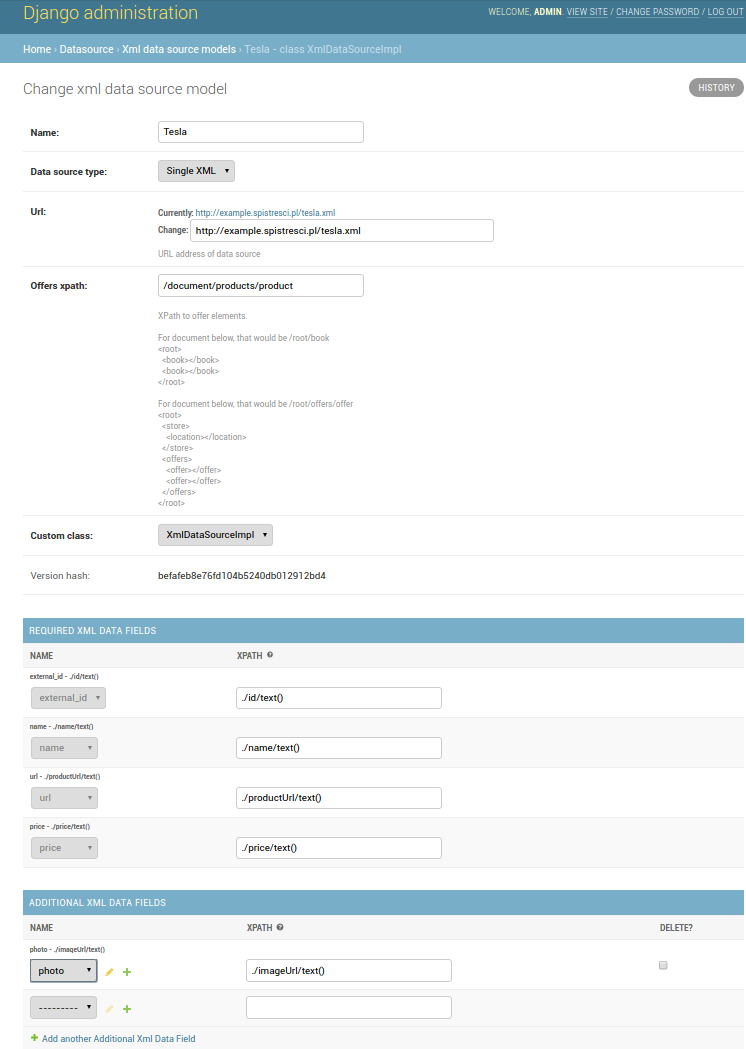
Configuration¶
Adding new Store¶
To create new Store, you have to have account with admin priviliges. Then, log in to admin pannel (<your website>/admin/) and go to Stores section.
Properties:
- Enabled
- If checked, Store will be updated according to schedule of defined jobs
- Name
- Name of store
- Url
- Url to main site of store. This is not an url to XML or API. This should be address to main site of Store.
- DataSource
- DataSource is responsible for providing information how to import data for specific Store. To have a possibility to choose any DataSource from dropdown list, you have to first define new DataSource in Admin Panel, as it is described below. Probably you will have to create seperate DataSource for each Store.
Adding new DataSource¶
Right now matadata about products/offers can be imported from XML files. However architecture of SpisTresci supports multiple formats of input data. If you need a support for different format of API, please create an Issue on our github. You can also provide a support for new formats on your own by providing custom classes which will be derived from DataSourceModel and DataSourceImpl classes.
To create DataSource for new Store, go to admin panel and click “+Add” next to DataSource of desired type.

Properties:
- Name
- Each type of DataSource should have own unique name. All other properties are specific for different types of DataSources. Please read documentation for specific DataSource type for more details.
XMLDataSource¶
- Data Source type
XMLDataSource is capable of extracting data not only from single XML file, but also from archives which contains multiple XML files. With Data Source type you can specify behaviour for file downloaded from specified url.
- Single XML
- The most basic case, when Store expose all offers by single XML file as API
- Url
- Address from which data will fetched periodically
- Offers root xpath
XPath to element which children are offers elements.
For document below, that would be
/root/book<root> <book></book> <book></book> </root>
and in that case, that would be
/root/offers/offer<root> <store> <location></location> </store> <offers> <offer></offer> <offer></offer> </offers> </root>
- Custom Class
Sometimes data provided by Store do not suit very well to assumptions which need to be made during design of database. For example, we assumed that each offer has unique integer id in Store database, or each offer has name no longer than 256 characters. For sure there are Stores, which can have offers with even longer names, or Stores which have alphanumeric ids.
In such cases, there is no other choice than write some additional code, which will handle those specific cases in desired way. You can find examples of such classes written in Python in spistresci/datasource/specific directory. Your new custom class should derived from DataSourceImpl (directly or indirectly).
XMLDataFields¶
- Required XML Data Fields
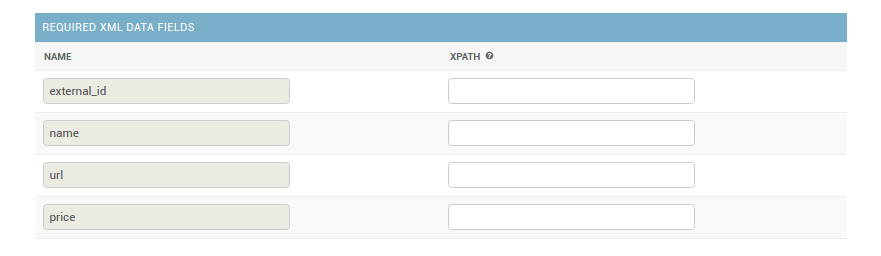
Right now there are exactly four required XML Data Fields - external_id, name, price, url. That means that you have to provide information (by xpath), how to extract those offer metadata. If Store which you want to add do not have any of Required XML Data Fields, there is no other way - you have to write your own Custom Class to hadle such weird case.
- external_id
- is an id of offer which Store uses in own database to identify specific offer (name of offer is not the best candidate for being a unique identifier, because there can be multiple offers with the same name).
- name (default=’‘)
Because offers have to be presented somehow to users, that is why we need something like name for each offer.
If xpath will not be properly resolved, default value will be used.
- price (default=Decimal(‘0.00’))
Each offer should have own price. If xpath will not be properly resolved, default value will be used.
If xpath will not be properly resolved, default value will be used.
- url (default=’‘)
We assume, that each offer has own url, where you can find details about it.
If xpath will not be properly resolved, default value will be used.
- Additional XML Data Fields
The great news is that you can store any data about offers/products in the database! :) The only thing which you have to do to choose custom datafield name from dropdown is create new Data source field name.
and then you will be able to choose this name from dropdown list and provide an information how to extract value of this property from XML document (by xpath)
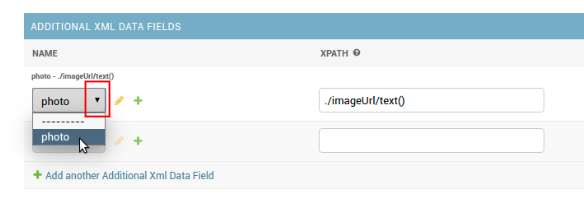
For example, to store information about size of product in your database, just create new field with name size (or ‘dimensions’ if you prefer - name of property do not have to be exactly the same as it is in XML document of specific store). You will be able to fetch all additional data stored in database via API.
XMLDataFields - XPath¶
XPath (XML Path Language) is a best way to specify how to exctract data from XML document. Let’s take a look on few examples. Having fallowing XML Document:
<document>
<company>
<ceo>Elon Musk</ceo>
<employees>13058</employees>
<address>
<city>Palo Alto</city>
<state>California</state>
<country>USA</country>
</address>
</company>
<offers>
<offer avail="0">
<id>1</id>
<model>Tesla Roadster</model>
<imageUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/sites/default/files/styles/blog-picture_2x_1400xvar_/public/0H8E6227_1.jpg</imageUrl>
</offer>
<offer avail="1">
<id>2</id>
<model>Tesla Model S</model>
<price>63400.00</price>
<offerUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/models</offerUrl>
<imageUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/tesla_theme/assets/img/models/section-initial.jpg</imageUrl>
</offer>
<offer avail="1">
<id>3</id>
<model>Tesla Model X</model>
<price>69300.00</price>
<offerUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/modelx</offerUrl>
<imageUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/tesla_theme/assets/img/modelx/section-exterior-profile.jpg</imageUrl>
</offer>
<offer avail="1">
<id>4</id>
<model>Tesla Model 3</model>
<price>35000.00</price>
<offerUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/model3</offerUrl>
<imageUrl>https://www.teslamotors.com/sites/default/files/images/model-3/gallery/gallery-1.jpg</imageUrl>
</offer>
</offers>
</document>
with xpath /document/offers/offer/model/text() you will get ['Tesla Roadster', 'Tesla Model S', 'Tesla Model X', 'Tesla Model 3'], and similarly with /document/offers/offer/price/text() you will get ['63400.00', '69300.00', '35000.00'] (please notice that we got only 3 prices, because ‘Tesla Roadster’ is not available and document do not describe it’s price).
Because of the structure of typical XML document like this, part /document/offers/offer may seem to be redundant. Actually, it is very important, because without it alghorithm would not know how to group extracted properties into properties of single offer.
To overcome this problem in that case /document/offers/offer should be specified as offers root xpath for whole XMLDataSource.
Thanks to that, all XML Data Field‘s xpaths can be simplified and replaced with relative xpaths. In that case that would be: ./model/text(), ./price/text().
Example of complete configuration¶